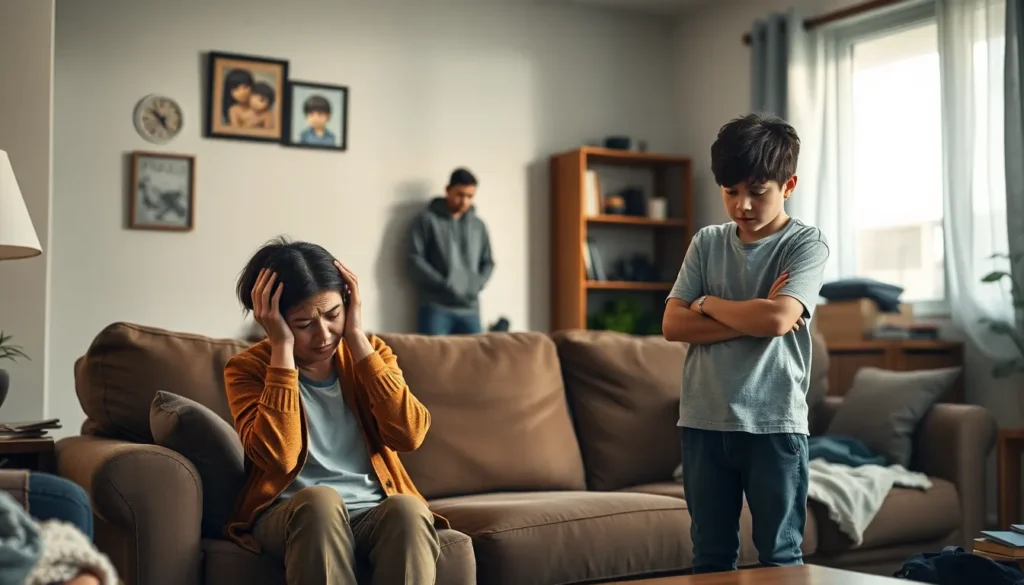
Addiction doesn’t just knock on the door; it barges in and rearranges the furniture, leaving chaos in its wake. Families often find themselves caught in a whirlwind of emotions, struggling to navigate the complexities of addiction while trying to hold it all together. It’s a wild ride, filled with love, frustration, and the occasional awkward family dinner where Uncle Joe insists he’s “fine” while holding a suspiciously large glass of something.
Understanding family dynamics in addiction is crucial. It’s not just about the person struggling with substance use; it’s about how their behavior impacts everyone around them. From enabling to codependency, each family member plays a role in this intricate dance. By exploring these dynamics, families can begin to heal and reclaim their lives, one step at a time. After all, laughter might not cure addiction, but it sure helps lighten the load.
family dynamics in addiction
Addiction significantly alters family dynamics, creating a chaotic atmosphere that affects all members. Families often face emotional turmoil while dealing with a loved one’s substance use, leading to distress and confusion. Specific roles emerge within the family system, such as the enabler, the caretaker, and the identified patient. Each family member’s behavior can influence the cycle of addiction.
Enablers frequently try to protect the addicted individual from the consequences of their actions, which can unintentionally prolong the addiction. Caretakers take on additional responsibilities, often sacrificing personal needs to manage family crises. The identified patient holds the central role of the person struggling with addiction, impacting family relationships profoundly.
Communication often breaks down in families affected by addiction, resulting in misunderstandings and resentment. Interaction patterns shift, creating an environment where feelings of anger and shame prevail. Addressing these dynamics requires honest dialogue and a willingness to confront uncomfortable truths.
Family therapy plays a vital role in recovery. Professionals facilitate conversations that encourage accountability and insight. With support, families can redefine their relationships and roles, enabling healthier interactions. Recovery is a collective process, and understanding family dynamics is crucial for healing.
Emphasizing self-care helps family members cope with the stress of their situation. Activities such as exercise, counseling, and support groups foster resilience. Families can regain a sense of control and stability by focusing on individual well-being alongside collective recovery efforts.
The Impact of Addiction on Family Structures
Addiction profoundly disrupts family structures, creating a chaotic environment that affects every member. Families experience emotional turmoil while trying to cope with a loved one’s substance use, leading to distress and confusion.
Roles Within the Family Unit
Different roles emerge in families affected by addiction. The enabler often protects the addicted individual from facing consequences. Caretakers assume additional responsibilities, sacrificing their own needs for family stability. The identified patient, or the individual struggling with addiction, becomes the focal point of the family’s dynamic. These roles perpetuate the cycle of addiction, creating a complex web of interactions that complicates recovery efforts. Families may feel trapped in these roles, hindering open communication and collaboration.
Emotional Responses and Coping Mechanisms
Families respond emotionally to addiction in various ways. Anxiety frequently arises from uncertainty about the future. Anger often bubbles beneath the surface when dealing with betrayal or disappointment. Additionally, guilt may plague family members, as they question their actions. Some adopt coping mechanisms such as avoidance or denial while others seek support through therapy or support groups. These emotional responses shape family interactions, where misunderstandings can create further tension. Establishing honest dialogue promotes healthier coping strategies and fosters a supportive environment for all members.
Communication Patterns in Families Affected by Addiction
Addiction creates complex communication patterns that significantly impact family dynamics. Families often find themselves trapped in cycles of interaction that hinder recovery.
Healthy vs. Unhealthy Communication
Healthy communication fosters understanding, support, and empathy. Open dialogue encourages family members to express feelings and share experiences without fear. Listening actively and validating concerns promotes connection. Unhealthy communication often manifests as blame, criticism, or avoidance. Families may engage in denial about the addiction, leading to misunderstandings. Emotional outbursts replace constructive conversations, which escalate tensions. Patterns of silence or withdrawal can make issues worse, as secrets thrive in silence. Recovery objectives benefit greatly from shifting communication styles to prioritize honesty and transparency.
The Role of Stigma and Shame
Stigma surrounding addiction deeply influences family communication. Many family members experience shame, which complicates their willingness to discuss addiction openly. Fear of judgment from outsiders often silences conversations. Families might conceal the addiction to protect their image, leading to isolation. These barriers discourage seeking help or participating in support groups. Addressing stigma helps reduce shame, allowing families to feel more comfortable sharing experiences. By recognizing and confronting these feelings, families can foster acceptance and understanding. Ultimately, breaking the cycle of stigma creates an environment conducive to healing and supports recovery efforts.
Interventions and Support for Families
Interventions and support are critical for families dealing with addiction. Seeking help fosters a nurturing environment, enabling family members to address underlying issues.
Therapy and Counseling Options
Therapy plays a valuable role in addiction recovery for families. Professional therapists can guide families through conversations that clarify feelings and encourage accountability. Each member learns to express their emotions in constructive ways. Individual therapy allows members to work on personal challenges while family therapy builds stronger collective relationships. Techniques like cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) assist in altering detrimental communication patterns. Additionally, engaging in couples therapy benefits relationships strained by addiction, offering tools for healthier interactions.
Support Groups and Community Resources
Support groups act as a lifeline for families navigating the challenges of addiction. Organizations like Al-Anon and Nar-Anon provide space for family members to share experiences and learn coping strategies. Meetings often focus on fostering resilience and breaking isolation. Family members benefit from hearing others’ stories and gaining insights into their feelings. Community resources, such as local counseling services and workshops, offer essential information and connections to additional support. Developing a network of understanding peers strengthens both individual well-being and collective recovery efforts.
Conclusion
Addiction’s impact on family dynamics is profound and multifaceted. Families often find themselves navigating a complex web of roles and emotions that can hinder recovery efforts. By prioritizing open communication and engaging in family therapy, they can shift these dynamics toward healthier interactions.
Self-care for family members is equally crucial in fostering resilience and stability. Embracing support groups and community resources can further enhance their journey toward healing. Through these efforts, families can break free from the cycle of addiction, creating a nurturing environment that promotes lasting recovery and healthier relationships.



